Understanding Replication In MySQL
March 17, 2024 · 1328 words · 7 min
MySQL Replication is a process where data from one MySQL database known as the master is copied over to one or more other databases called replicas or slaves. In this article, we’ll learn what replication is, how to enable replication, replication modes and replication forms.
What is replication in MySQL?
MySQL replication refers to the transfer of data from one MySQL server (master) to another MySQL server or multiple MySQL servers through the network by logs, and then replay the transferred logs on the slave to achieve the purpose of synchronization with the master data.
The working principle of replication is quite simple. Let’s take a look.
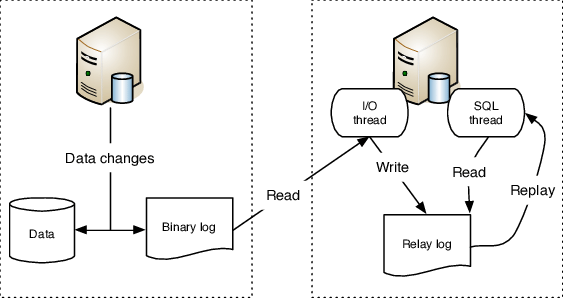
In order to enable replication, it is necessary for the MySQL master to enable the binlog feature.
On the slave server, the
change master tocommand needs to be executed along with relevant context information such as the binlog filename and offset.The slave server consists of two threads: the I/O thread and the SQL thread.
The I/O thread is responsible for establishing a connection with the master server and receiving the binlog data. Once the I/O thread successfully connects to the master, the master server initiates a “dump thread” which retrieves the requested binlog data. The I/O thread then copies and saves this binlog data to its own relay log.
The SQL thread is responsible for reading and replaying the data stored in the relay log. It processes the data and writes it to the slave server’s own database.
Replication Forms
Typically, there are the following forms in replication, each form has its scenes to be used.
- Master to slave
- Master to master
- Cascading
Master to slave
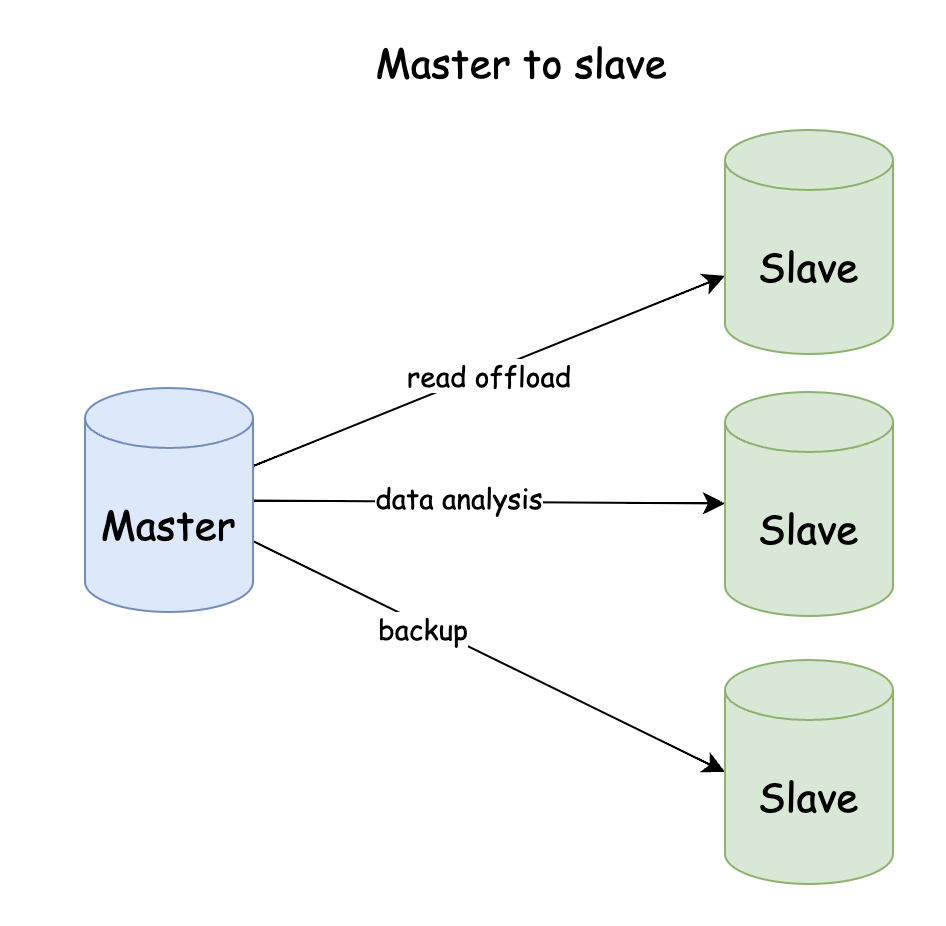
Master-slave replication is the most commonly used replication mode. As shown in the figure, we have 1 master server and 3 slave servers. The slave servers are responsible for sharing the read load, data analysis and data backup functions of the master server.
Master to master
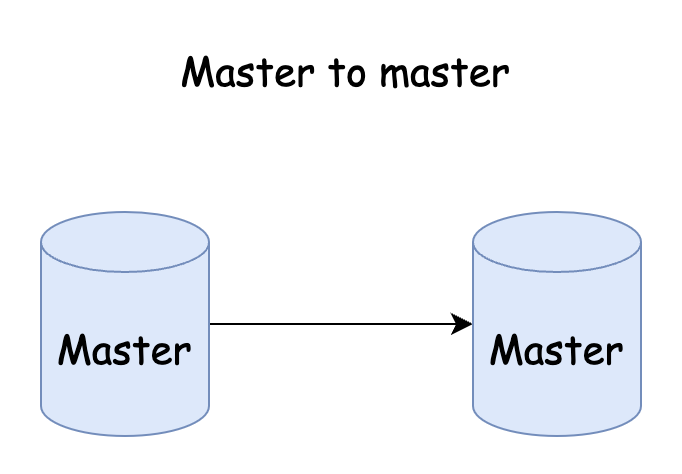
MySQL Master-Master Replication is a database replication mode in which two or more MySQL servers can act as master servers and slave servers for each other to achieve two-way synchronization of data.
Cascading
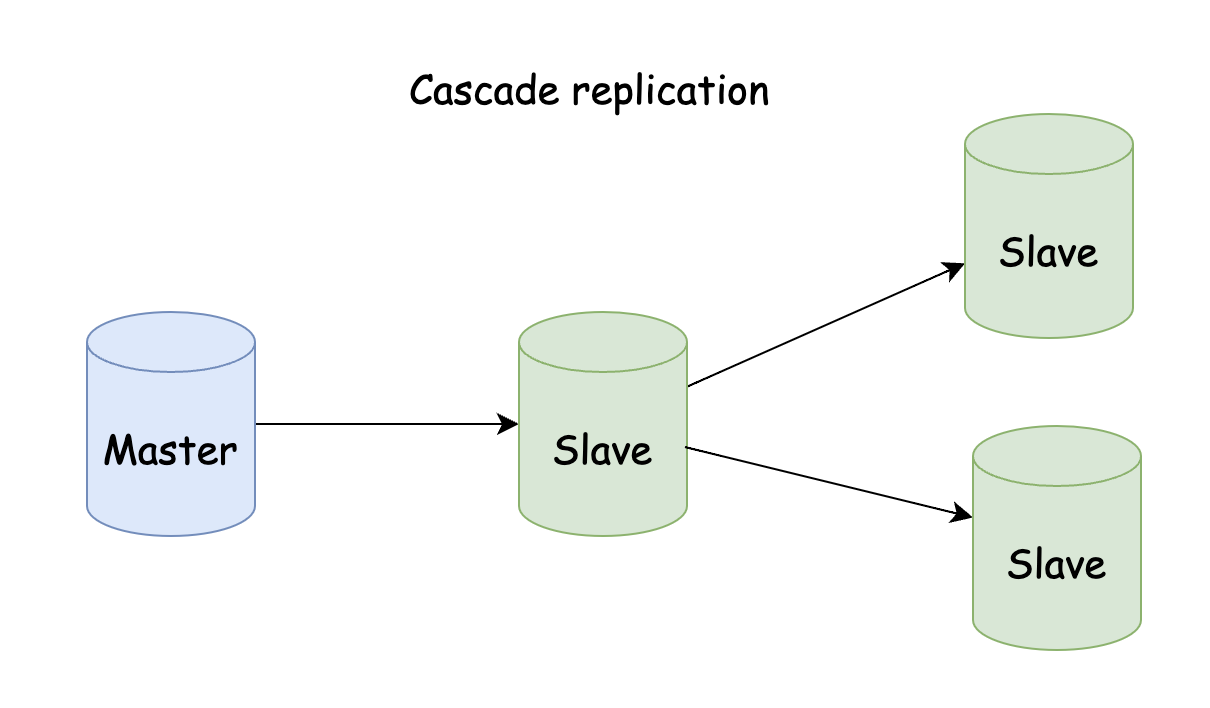
Cascading replication is the master server, which only synchronizes data to one slave server, and then the slave server synchronizes data to all slave servers in the backend, reducing the write pressure of the master server and the network IO of copying data.
Replication Modes
There are 3 replication modes in MySQL:
- Asynchronous replication
- Semi-synchronous replication
- Synchronous replication
Asynchronous replication
Asynchronous replication is the default mode in MySQL.The integrity of the data depends on the binlog of the master database. As long as the binlog of the main database is not lost, even if the master database is down, we can still manually synchronize the lost part of the data to the slave database through binlog.
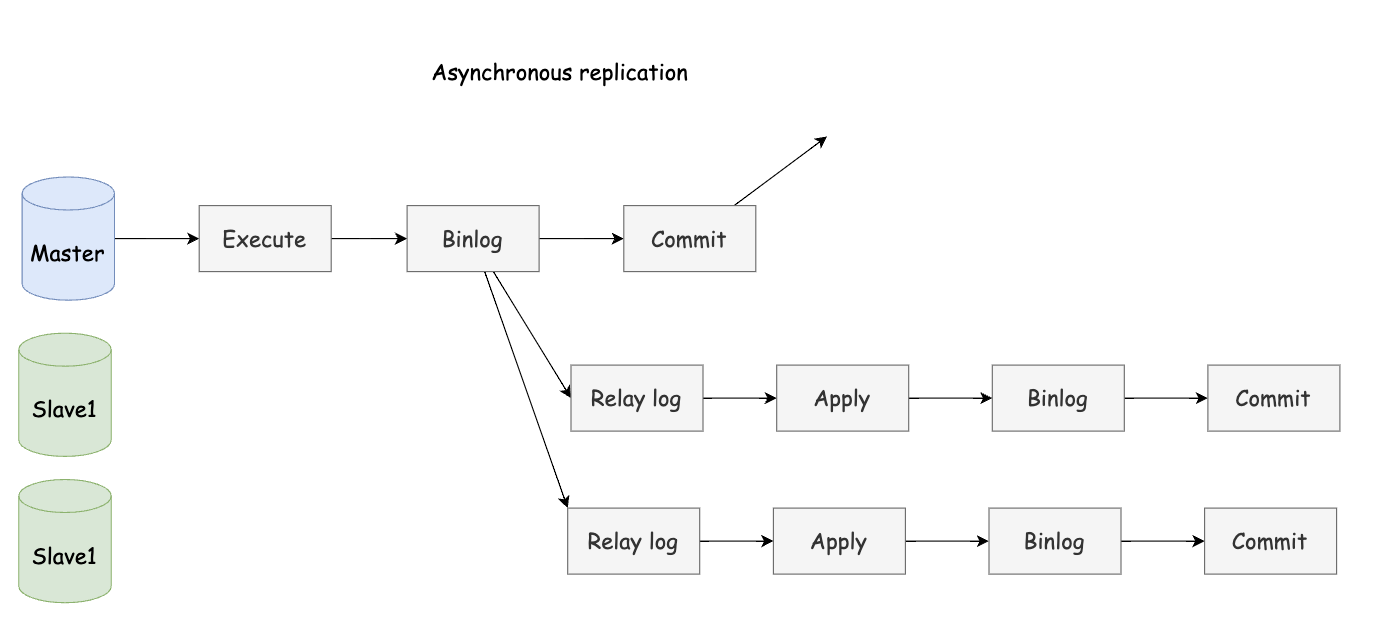
In asynchronous replication mode, the master generates binlog and synchronizes it to all slaves, and then directly commits the transaction. Asynchronous replication has the highest performance, but if the master server crashes before receiving the binlog from the slave server, data will be lost.
Semi-synchronous replication
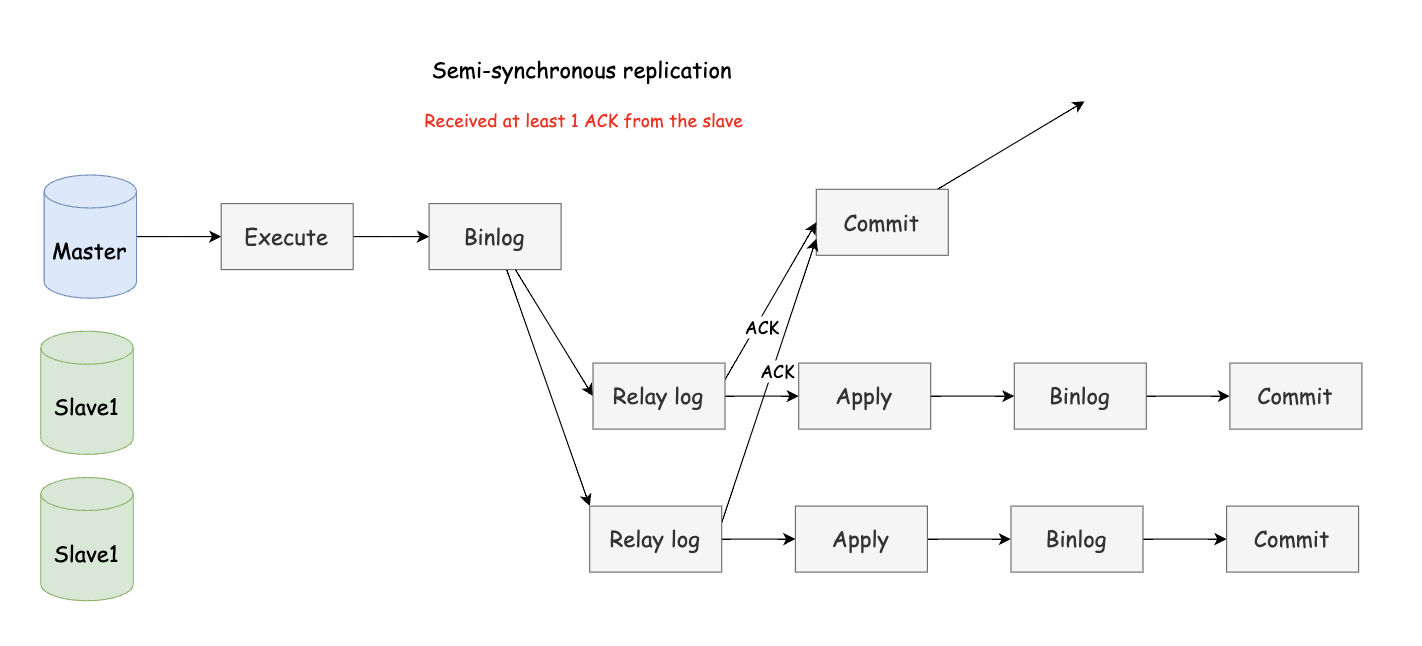
After the master completes the transaction submitted by the client, it must wait for at least one slave to receive the binlog and write the data to the relay log before returning a successful result to the client. The semi-synchronous replication mode improves data availability compared to the asynchronous mode, but it also produces a certain performance delay, which requires at least the round-trip time of a TCP/IP connection.
Synchronous replication
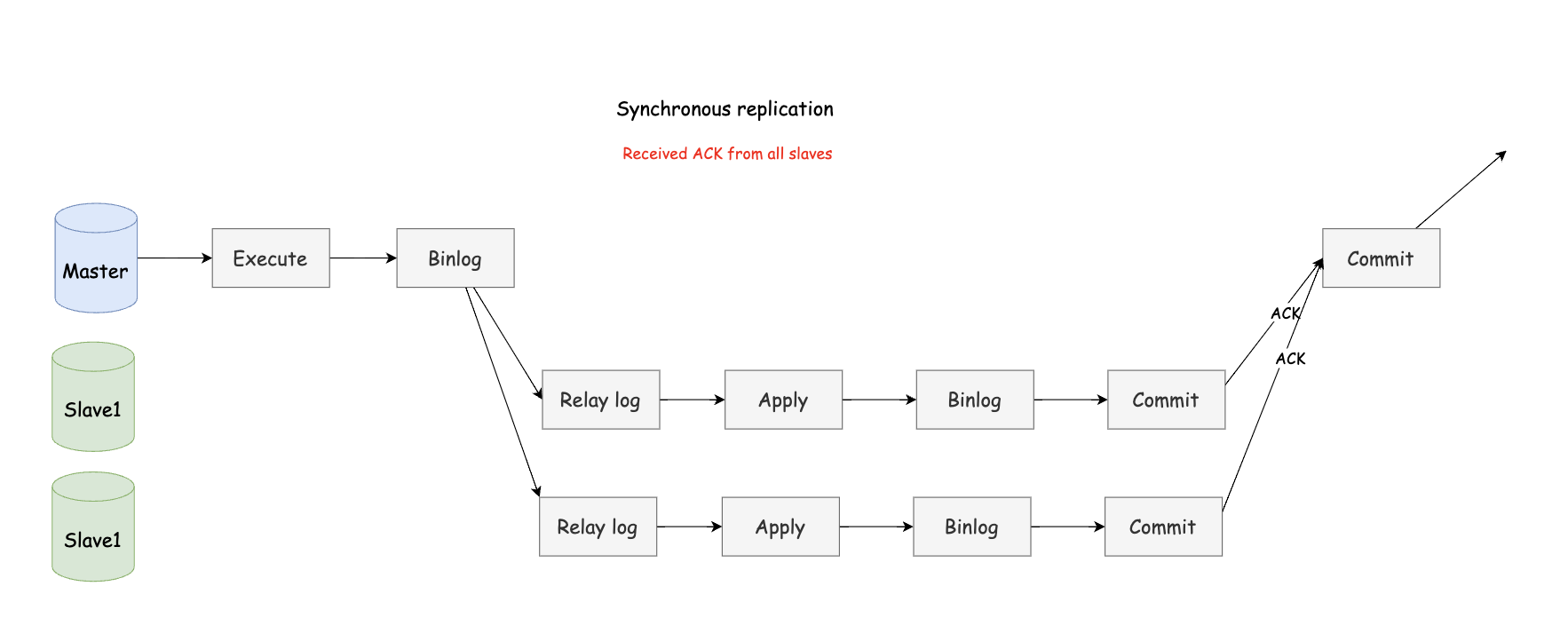
After the master completes a transaction, all slaves are required to complete the transaction before the processing results can be returned to the client. Therefore, although the data consistency of fully synchronous replication is guaranteed, the master needs to wait for all slaves to complete a transaction, and the performance will be relatively low.
How to enable MySQL replication?
Modify the configuration of master:
#Main database ID number server_id = 1 #Enable binary log log-bin = mysql-binRestart the master and create a replication account:
grant replication slave on *.* to 'ACCOUNT_NAME'@'SLAVE_HOST' identified by 'ACCOUNT_PASSWORD'; flush privileges;Check the status of master:
show master status\G; ***************** 1. row **************** File: mysql-bin.00001 Position: 10000Modify the configuration of slave:
server_id = 2 # choose a different server_id to master log-bin = mysql-binInitialize replication on slave:
change master to master_host='MASTER_HOST',master_user='ACCOUNT_NAME',master_password='ACCOUNT_PASSWORD',master_log_file='mysql-bin.00001',master_log_pos=10000; start slave;Check the status of slave:
show slave status\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: Master_User: Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.00001 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 10000 Relay_Log_File: db2-relay-bin.00002 Relay_Log_Pos: 10000 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.00001 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes Replicate_Do_DB: Replicate_Ignore_DB:When both Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are running, replication works normally, otherwise the cause needs to be investigated.
Canal
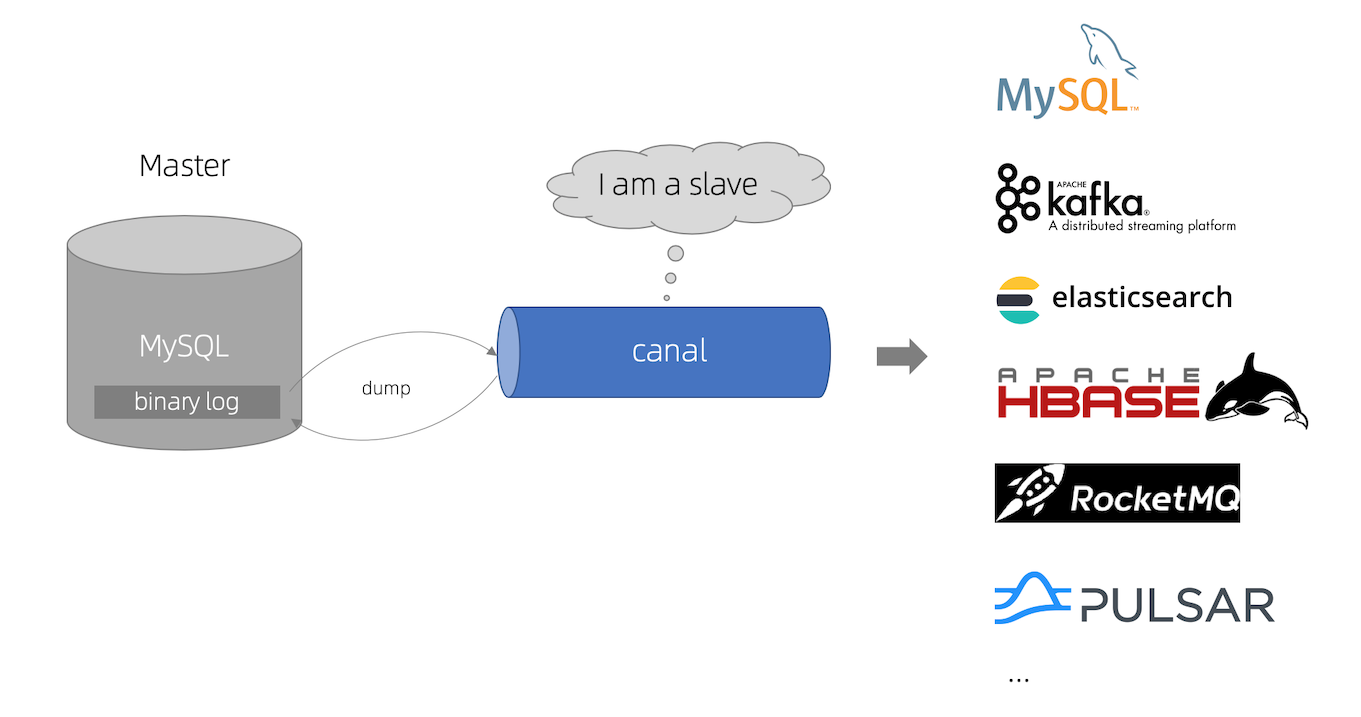
Sometimes, we need to synchronize mysql data to other data systems, such as ElasticSearch. The traditional way is to write business code in MySQL and ElasticSearch at the same time, which is intrusive to the business code. Alibaba’s open source Canal solves this problem. Canal is forged as a slave, uses the MySQL synchronization protocol to interact with the master, and sends the master’s data to message queues, such as Kafka, Pulsar, etc.
Note: Canal requires master server uses the ROW binlog-format.
binlog-format
MySQL supports three binlog formats:
- Statement: In this format, every SQL statement that modifies data is recorded in the binlog.
- Row: In Row format, only the data modifications are saved in the binlog, without recording the SQL statements.
- Mixed: Mixed format is a combination of Statement and Row formats.
Statement Format
In Statement format, only the executed SQL statements are recorded in the binlog. It reduces the amount of binlog logs, minimizes IO operations, and improves system performance.
However, a drawback of the Statement format is that it only records the SQL statements, not the actual changes made to the data. This can lead to inconsistencies if certain SQL statements contain functions or non-deterministic operations. For example, if the uuid() function is used, it generates a random string each time it is executed. As a result, the UUID recorded in the master may differ from the one generated when the statement is executed on the slave, causing data inconsistency.
Row Format
In Row format, each row of data modifications is recorded in the binlog. This provides a more detailed and accurate representation of the changes made.
However, the Row format has the drawback of generating a large amount of binlog data, especially for operations like batch updates, table-wide deletions, and alter table statements. Since every change in each row of data needs to be recorded, it can lead to a significant increase in log size and potential IO performance issues.
Mixed Format
Mixed format is a combination of Statement and Row formats. In Mixed mode, the system automatically determines whether to use Statement or Row format based on the type of operation. Generally, statement modifications use Statement format to save binlog, but for certain operations that cannot be accurately replicated using Statement format, Row format is used to ensure the accuracy of binlog.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MySQL replication is a powerful feature that allows data to be transferred from one MySQL server to another, enabling synchronization between multiple databases. Replication can be configured in different forms, such as master-slave, master-master, and cascading, each with its own use cases and benefits.
There are also different replication modes available, including asynchronous, semi-synchronous, and synchronous replication. These modes provide varying levels of data consistency and performance, allowing users to choose the option that best suits their requirements.
In addition to native MySQL replication, tools like Canal can be used to synchronize MySQL data with other data systems, such as ElasticSearch. Canal acts as a slave and leverages the MySQL synchronization protocol to capture and send data changes to message queues.
Overall, understanding MySQL replication and its various aspects, including forms, modes, configuration, and binlog formats, empowers database administrators and developers to design robust and scalable systems that meet their specific needs.