Retrieval-Augmented Generation
April 24, 2024 · 759 words · 4 min
In the era of information explosion, we are faced with the challenge of vast amounts of data. Retrieving useful information from this data is becoming increasingly difficult for people. To address this issue, researchers have proposed a novel technology called RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
RAG combines the methods of retrieval and generation to make information extraction from large-scale data more efficient and accurate.
This article will introduce the definition, working principle, and problems addressed by RAG.
What is RAG?
RAG is a pre-trained deep learning model designed to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of data retrieval by combining retrieval and generation methods. It is an advancement of the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) model that incorporates a retrieval mechanism, allowing the model to leverage external sources of knowledge during the generation process. Specifically, the RAG architecture consists of two main components: the Retriever and the Generator.
The Retriever is responsible for retrieving relevant information from large-scale datasets. The Generator utilizes the retrieved information to generate responses. This combination allows RAG to obtain more accurate and relevant content during the generation process, resulting in more valuable outcomes.
What problems does RAG solve?
Traditional retrieval-based methods often face two main challenges: information overload and the accuracy of results. Information overload refers to the difficulty of finding relevant information within large-scale datasets, while the accuracy of results can be compromised due to limitations in the generation model, resulting in generated content that may lack relevance. RAG effectively addresses these two problems by introducing a retrieval mechanism.
- Firstly, by using the Retriever, RAG can quickly and accurately retrieve relevant information from large-scale datasets, alleviating the issue of information overload. Secondly, the Generator uses the retrieved information to guide the generation process, resulting in content that is more relevant and accurate.
- Another issue is the controllability of traditional generation models. In certain application scenarios, users need some level of control over the generated results to meet specific requirements. Traditional generation models often lack this controllability.
- However, by combining the retrieved information with the Generator, RAG enables users to guide the model’s behavior during the generation process, providing better control over the generated results.
Working Principle of RAG
The working principle of RAG can be divided into three main steps: preprocessing, retrieval, and generation.
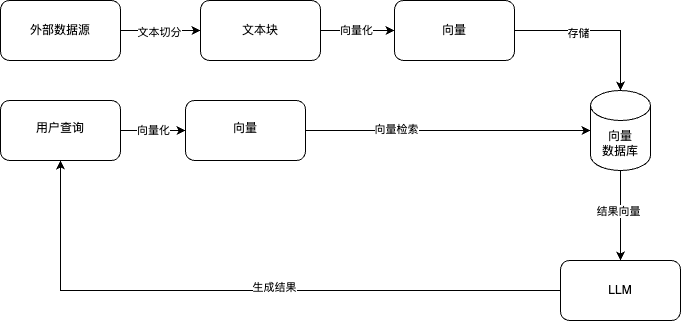
Preprocessing Phase
In the preprocessing phase, external data sources need to be vectorized and stored in a vector database. For example, for large text data, it needs to be segmented into text chunks, each of which is vectorized and stored.
Retrieval Phase
In the retrieval phase, RAG utilizes the Retriever to find information relevant to the query from a large-scale external dataset. The Retriever typically relies on traditional information retrieval methods such as inverted indexes and vector retrieval. It takes the query as input and returns relevant documents or snippets related to the query.> External datasets need to be vectorized in advance and stored in a vector database.
Generation Phase
In the generation phase, RAG uses the Generator to generate responses based on the retrieved information. The Generator is usually a pre-trained language model such as the GPT model. It takes two inputs: the query and the retrieved information. The query guides the generation topic or intent, while the retrieved information provides context and relevance. The Generator generates a response based on these inputs and iteratively refines the results throughout the generation process. In the generation process, RAG can also enhance controllability by introducing additional constraints or guiding information. For example, specific keywords or conditions can be used to constrain the content or style of the generated results. This allows users to have better control over the generated results to meet specific requirements.
Conclusion
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is a retrieval-augmented generation technology that improves the accuracy and efficiency of information extraction from large-scale data by combining retrieval and generation methods. It addresses the problems of information overload and result accuracy by introducing a retrieval mechanism and provides better controllability. This approach opens up new possibilities in fields such as information retrieval and automated content generation.
With the continuous development of technology, RAG has a promising future in the fields of information retrieval and content generation. It is expected to provide users with more accurate, relevant, and controllable results, thereby enhancing user experience and meeting specific needs. However, RAG still faces challenges, such as handling multimodal data and improving the diversity of generated results.
I hope this article provides readers with a preliminary understanding of RAG.
In the next installment, I will demonstrate how to build a retrieval engine based on Llama3. Stay tuned!